Simulation of surface enhanced vibrational spectroscopy
T. Colleu-Banse1, A. Fekete1, L. Henrard1
1 Department of Physics and NISM Institute, University of Namur
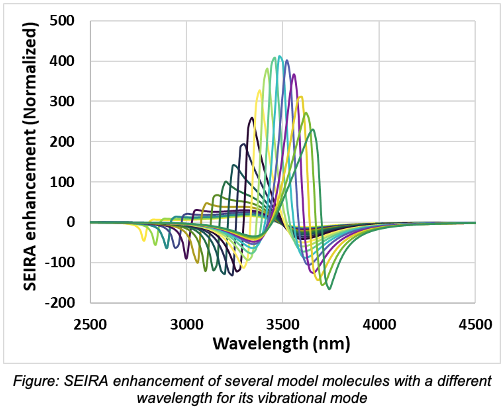
Surface Enhance Infrared Absorption (SEIRA) is an experimental method where trace amounts of a compound are detected by enhancing their absorption in the infrared spectrum1. This enhancement is a result of the interaction of the molecules with a localized plasmon, usually from a metallic nano-particle. A common hypothesis is that the molecule is mainly affected by the high local electric-field resulting from the plasmonic resonance, with some sources suggesting that the enhancement is proportional to the square of the electric-field intensity2,3. However, the exact nature of this interaction Has not been analysed into details.
Here we simulate this electromagnetic interaction within a Discrete Dipole Approximation. Those simulations yield similar behaviour to what can be found in experimental studies with a decrease of the overall cross-section absorption at the molecule resonance when it coincides with the plasmonic resonance. This decrease is tied to the effect of the molecule on the polarization of the nano-particle according to our results. This is unexpected as the molecular polarizability is very small compared to the plasmonic response of the metallic nano-particle. This work sheds a brighter light on the mechanism of SEIRA.
- Dong, L., Yang, X., Zhang, C., Cerjan, B., Zhou, L., Tseng, M.L., Zhang, Y., Alabastri, A., Nordlander, P., Halas, N.J., Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 5768–5774.
- Neubrech, F., Beck, S., Glaser, T., Hentschel, M., Giessen, H., Pucci, A., ACS Nano. 2014, 8, 6250–6258.
- Neuman, T., Huck, C., Vogt, J., Neubrech, F., Hillenbrand, R., Aizpurua, J., Pucci, A., J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 26652–26662.
